International standardisation of electronic fee collection
EFC standards provide effective support for procurement and interoperability, and underpin the European electronic toll service legislation.
Context
Electronic fee collection (EFC) is an overall notion used to designate ICT solutions that automatically, and without stopping, collect road user charges. EFC systems allow effective charging of road vehicles and support a broad variety of pricing policies.
There are many EFC systems in Europe today. However, most of them have been developed and expanded on a regional basis creating different variants between different nations. In order to reap the full benefits of EFC systems they need to be interoperable, allowing a vehicle to pay charges in different countries using a single on-board unit and a single contract.
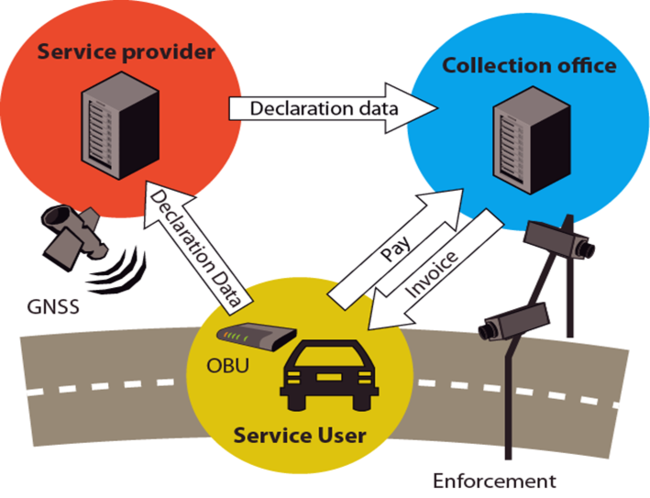
EFC standardisation
A Rapp staff member, as the appointed convenor, coordinates since 2004 the development of the worldwide and European EFC standards in ISO and CEN.
The EFC standards provide key elements for achieving interoperability. They are used in more than 40 countries and 150 systems around the world. More than 100 million compliant on-board units and 40 000 of compliant roadside equipment and are deployed around the world.
The EFC standards define information exchanges between toll chargers and service providers. They cover systems based on dedicated short-range communication (DSRC), global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and smart card technologies. They include “requirements” and associated test procedures in order to support conformity evaluation of products. Charging performance metrics and examination framework support service level agreements. The suite of standards also includes security guidelines that can be useful in the preparation or evaluation of security requirements.